Хеш-таблица в C/C++: полная реализация
Development | Комментировать запись
Хеш-таблица в C/C++ (ассоциативный массив) — это структура данных, которая сопоставляет ключи со значениями и использует хеш-функцию для вычисления индексов ключа.
Индекс хеш-таблицы позволяет нам сохранить значение в соответствующем месте.
Если два разных ключа получают один и тот же индекс, для учета подобных коллизий мы должны использовать другие структуры данных (сегменты).
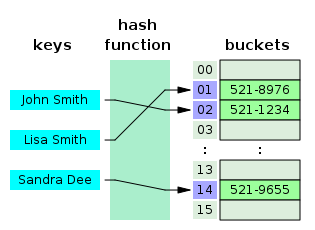
Главное преимущество использования хеш-таблицы – очень короткое время доступа. Конфликты иногда могут возникать, но шансы практически равны нулю, если выбрать очень хорошую хэш-функцию.
Итак, в среднем временная сложность представляет собой постоянное время доступа O(1) – это называется амортизационной временной сложностью.
C++ STL (стандартная библиотека шаблонов) использует структуру данных std::unordered_map(), которая реализует все эти функции хэш-таблицы.
Однако уметь строить хеш-таблицы с нуля – навык важный и полезный, и именно этим мы займемся в данном мануале.
Давайте разберемся подробнее в деталях реализации таблиц. Любая реализация хеш-таблицы состоит из следующих трех компонентов:
- Хорошая хеш-функция для сопоставления ключей со значениями.
- Структура данных хеш-таблицы, поддерживающая операции вставки, поиска и удаления.
- Структура данных для учета конфликтов ключей
Выбор хэш-функции
Первый шаг — выбрать достаточно хорошую хеш-функцию с низкой вероятностью возникновения коллизии.
Но для иллюстрации в этом мануале мы сделаем все наоборот – выберем плохую функцию и посмотрим, что получится.
В этой статье мы будем работать только со строками (или массивами символов).
Мы будем использовать очень простую хеш-функцию, которая просто суммирует значения ASCII строки. Эта функция позволит нам продемонстрировать, как обрабатывать коллизии.
#define CAPACITY 50000 // Size of the Hash Table
unsigned long hash_function(char* str) {
unsigned long i = 0;
for (int j=0; str[j]; j++)
i += str[j];
return i % CAPACITY;
}
Вы можете проверить эту функцию для разных строк и увидеть, возникают коллизии или нет. Например, строки «Hel» и «Cau» будут конфликтовать, так как они имеют одинаковое значение ASCII.
Примечание: Таблица должна вернуть число в пределах своей емкости. В противном случае мы можем получить доступ к несвязанной области памяти, что приведет к ошибке.
Определение структуры данных хеш-таблицы
Хеш-таблица — это массив элементов, которые сами по себе являются парой {ключ: значение}.
Давайте теперь определим структуру нашего элемента.
typedef struct Ht_item Ht_item;
// Define the Hash Table Item here
struct Ht_item {
char* key;
char* value;
};
Теперь хеш-таблица имеет массив указателей, которые сами ведут на Ht_item, так что получается двойной указатель.
Помимо этого, мы также будем отслеживать количество элементов в хеш-таблице с помощью count и сохранять размер таблицы в size.
typedef struct HashTable HashTable;
// Define the Hash Table here
struct HashTable {
// Contains an array of pointers
// to items
Ht_item** items;
int size;
int count;
};
Создание хеш-таблицы и ее элементов
Чтобы создать в памяти новую хеш-таблицу и ее элементы, нам нужны функции.
Сначала давайте создадим элементы. Это очень просто делается: нам нужно лишь выделить память для ключа и значения и вернуть указатель на элемент.
Ht_item* create_item(char* key, char* value) {
// Creates a pointer to a new hash table item
Ht_item* item = (Ht_item*) malloc (sizeof(Ht_item));
item->key = (char*) malloc (strlen(key) + 1);
item->value = (char*) malloc (strlen(value) + 1);
strcpy(item->key, key);
strcpy(item->value, value);
return item;
}
Теперь давайте напишем код для создания таблицы. Этот код выделяет память для структуры-оболочки HashTable и устанавливает для всех ее элементов значение NULL (поскольку они не используются).
HashTable* create_table(int size) {
// Creates a new HashTable
HashTable* table = (HashTable*) malloc (sizeof(HashTable));
table->size = size;
table->count = 0;
table->items = (Ht_item**) calloc (table->size, sizeof(Ht_item*));
for (int i=0; i<table->size; i++)
table->items[i] = NULL;
return table;
}
Мы почти закончили с этой частью. Как программист C/C++, вы обязаны освобождать выделенную память с помощью malloc(), calloc().
Давайте же напишем функции, которые освобождают элемент и всю таблицу.
void free_item(Ht_item* item) {
// Frees an item
free(item->key);
free(item->value);
free(item);
}
void free_table(HashTable* table) {
// Frees the table
for (int i=0; i<table->size; i++) {
Ht_item* item = table->items[i];
if (item != NULL)
free_item(item);
}
free(table->items);
free(table);
}
Итак, мы завершили работу над нашей функциональной хеш-таблицей. Давайте теперь начнем писать методы insert(), search() и delete().
Вставка в хеш-таблицу
Сейчас мы создадим функцию ht_insert(), которая выполнит задачу вставки за нас.
Она принимает в качестве параметров указатель HashTable, ключ и значение.
void ht_insert(HashTable* table, char* key, char* value);
Далее нужно выполнить определенные шаги, связанные с функцией вставки.
Создать элемент на основе пары {ключ : значение}.
- Вычислить индекс на основе хеш-функции
- Путем сравнения ключа проверить, занят ли данный индекс или еще нет.
- Если он не занят, мы можем напрямую вставить его в index
- В противном случае возникает коллизия, и нам нужно ее обработать
О том, как обрабатывать коллизии, мы поговорим немного позже, после того, как создадим исходную модель.
Первый шаг прост. Мы напрямую вызываем create_item(key, value).
int index = hash_function(key);
Второй и третий шаги для получения индекса используют hash_function(key). Если мы вставляем ключ в первый раз, элемент должен быть NULL. В противном случае либо точная пара «ключ: значение» уже существует, либо это коллизия.
В этом случае мы определяем другую функцию handle_collision(), которая, как следует из названия, обработает эту потенциальную коллизию.
// Create the item
Ht_item* item = create_item(key, value);
// Compute the index
int index = hash_function(key);
Ht_item* current_item = table->items[index];
if (current_item == NULL) {
// Key does not exist.
if (table->count == table->size) {
// Hash Table Full
printf("Insert Error: Hash Table is full\n");
free_item(item);
return;
}
// Insert directly
table->items[index] = item;
table->count++;
}
Давайте рассмотрим первый сценарий, где пара «ключ: значение» уже существует (то есть такой же элемент уже был вставлен в таблицу ранее). В этом случае мы всего лишь должны обновить значение элемента, просто присвоить ему новое значение.
if (current_item == NULL) {
....
....
}else {
// Scenario 1: We only need to update value
if (strcmp(current_item->key, key) == 0) {
strcpy(table->items[index]->value, value);
return;
}
else {
// Scenario 2: Collision
// We will handle case this a bit later
handle_collision(table, item);
return;
}
}
Итак, функция вставки (без коллизий) теперь выглядит примерно так:
void handle_collision(HashTable* table, Ht_item* item) {
}
void ht_insert(HashTable* table, char* key, char* value) {
// Create the item
Ht_item* item = create_item(key, value);
Ht_item* current_item = table->items[index];
if (current_item == NULL) {
// Key does not exist.
if (table->count == table->size) {
// Hash Table Full
printf("Insert Error: Hash Table is full\n");
return;
}
// Insert directly
table->items[index] = item;
table->count++;
}
else {
// Scenario 1: We only need to update value
if (strcmp(current_item->key, key) == 0) {
strcpy(table->items[index]->value, value);
return;
}
else {
// Scenario 2: Collision
// We will handle case this a bit later
handle_collision(table, item);
return;
}
}
}
Поиск элементов в хеш-таблице
Если мы хотим проверить правильность вставки, мы должны определить функцию поиска, которая проверяет, существует ключ или нет, и возвращает соответствующее значение, если он существует.
char* ht_search(HastTable* table, char* key);
Логика очень проста. Функция просто переходит к элементам, котороые не являются NULL, и сравнивает ключ. В противном случае она вернет NULL.
char* ht_search(HashTable* table, char* key) {
// Searches the key in the hashtable
// and returns NULL if it doesn't exist
int index = hash_function(key);
Ht_item* item = table->items[index];
// Ensure that we move to a non NULL item
if (item != NULL) {
if (strcmp(item->key, key) == 0)
return item->value;
}
return NULL;
}
Тестирование базовой модели
Давайте проверим, правильно ли работает то, что мы муже написали. Для этого мы используем программу-драйвер main().
Чтобы проиллюстрировать, как все работает, добавим еще одну функцию print_table(), которая выводит хеш-таблицу.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define CAPACITY 50000 // Size of the Hash Table
unsigned long hash_function(char* str) {
unsigned long i = 0;
for (int j=0; str[j]; j++)
i += str[j];
return i % CAPACITY;
}
typedef struct Ht_item Ht_item;
// Define the Hash Table Item here
struct Ht_item {
char* key;
char* value;
};
typedef struct HashTable HashTable;
// Define the Hash Table here
struct HashTable {
// Contains an array of pointers
// to items
Ht_item** items;
int size;
int count;
};
Ht_item* create_item(char* key, char* value) {
// Creates a pointer to a new hash table item
Ht_item* item = (Ht_item*) malloc (sizeof(Ht_item));
item->key = (char*) malloc (strlen(key) + 1);
item->value = (char*) malloc (strlen(value) + 1);
strcpy(item->key, key);
strcpy(item->value, value);
return item;
}
HashTable* create_table(int size) {
// Creates a new HashTable
HashTable* table = (HashTable*) malloc (sizeof(HashTable));
table->size = size;
table->count = 0;
table->items = (Ht_item**) calloc (table->size, sizeof(Ht_item*));
for (int i=0; i<table->size; i++)
table->items[i] = NULL;
return table;
}
void free_item(Ht_item* item) {
// Frees an item
free(item->key);
free(item->value);
free(item);
}
void free_table(HashTable* table) {
// Frees the table
for (int i=0; i<table->size; i++) {
Ht_item* item = table->items[i];
if (item != NULL)
free_item(item);
}
free(table->items);
free(table);
}
void handle_collision(HashTable* table, unsigned long index, Ht_item* item) {
}
void ht_insert(HashTable* table, char* key, char* value) {
// Create the item
Ht_item* item = create_item(key, value);
// Compute the index
unsigned long index = hash_function(key);
Ht_item* current_item = table->items[index];
if (current_item == NULL) {
// Key does not exist.
if (table->count == table->size) {
// Hash Table Full
printf("Insert Error: Hash Table is full\n");
// Remove the create item
free_item(item);
return;
}
// Insert directly
table->items[index] = item;
table->count++;
}
else {
// Scenario 1: We only need to update value
if (strcmp(current_item->key, key) == 0) {
strcpy(table->items[index]->value, value);
return;
}
else {
// Scenario 2: Collision
// We will handle case this a bit later
handle_collision(table, index, item);
return;
}
}
}
char* ht_search(HashTable* table, char* key) {
// Searches the key in the hashtable
// and returns NULL if it doesn't exist
int index = hash_function(key);
Ht_item* item = table->items[index];
// Ensure that we move to a non NULL item
if (item != NULL) {
if (strcmp(item->key, key) == 0)
return item->value;
}
return NULL;
}
void print_search(HashTable* table, char* key) {
char* val;
if ((val = ht_search(table, key)) == NULL) {
printf("Key:%s does not exist\n", key);
return;
}
else {
printf("Key:%s, Value:%s\n", key, val);
}
}
void print_table(HashTable* table) {
printf("\nHash Table\n-------------------\n");
for (int i=0; i<table->size; i++) {
if (table->items[i]) {
printf("Index:%d, Key:%s, Value:%s\n", i, table->items[i]->key, table->items[i]->value);
}
}
printf("-------------------\n\n");
}
int main() {
HashTable* ht = create_table(CAPACITY);
ht_insert(ht, "1", "First address");
ht_insert(ht, "2", "Second address");
print_search(ht, "1");
print_search(ht, "2");
print_search(ht, "3");
print_table(ht);
free_table(ht);
return 0;
}
В результате мы получим:
Key:1, Value:First address Key:2, Value:Second address Key:3 does not exist Hash Table ------------------- Index:49, Key:1, Value:First address Index:50, Key:2, Value:Second address -------------------
Замечательно! Кажется, все работает так, как мы и ожидали. Теперь давайте перейдем к обработке коллизий.
Разрешение коллизий
Существуют различные способы разрешения коллизии. Мы рассмотрим метод под названием «метод цепочек», целью которого является создание независимых цепочек для всех элементов с одинаковым хэш-индексом.
Мы создадим эти цепочки с помощью связных списков.
Всякий раз, когда возникает коллизия, мы добавляем дополнительные элементы, которые конфликтуют с одним и тем же индексом в списке переполненных бакетов. Таким образом, нам не придется удалять какие-либо существующие записи из таблицы.
Поскольку связные списки имеют временную сложность O(n) для вставки, поиска и удаления, при возникновении коллизии время доступа в наихудшем случае тоже будет O(n). Этот метод хорошо подходит для работы с таблицами небольшой емкости.
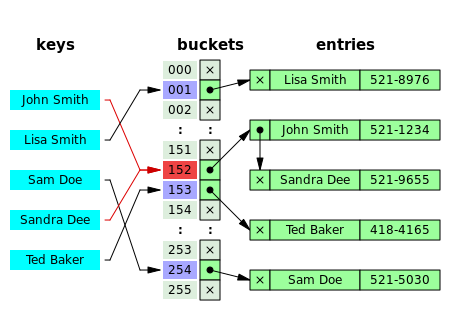
Давайте же приступим к реализации связанного списка.
typedef struct LinkedList LinkedList;
// Define the Linkedlist here
struct LinkedList {
Ht_item* item;
LinkedList* next;
};
LinkedList* allocate_list () {
// Allocates memory for a Linkedlist pointer
LinkedList* list = (LinkedList*) malloc (sizeof(LinkedList));
return list;
}
LinkedList* linkedlist_insert(LinkedList* list, Ht_item* item) {
// Inserts the item onto the Linked List
if (!list) {
LinkedList* head = allocate_list();
head->item = item;
head->next = NULL;
list = head;
return list;
}
else if (list->next == NULL) {
LinkedList* node = allocate_list();
node->item = item;
node->next = NULL;
list->next = node;
return list;
}
LinkedList* temp = list;
while (temp->next->next) {
temp = temp->next;
}
LinkedList* node = allocate_list();
node->item = item;
node->next = NULL;
temp->next = node;
return list;
Ht_item* linkedlist_remove(LinkedList* list) {
// Removes the head from the linked list
// and returns the item of the popped element
if (!list)
return NULL;
if (!list->next)
return NULL;
LinkedList* node = list->next;
LinkedList* temp = list;
temp->next = NULL;
list = node;
Ht_item* it = NULL;
memcpy(temp->item, it, sizeof(Ht_item));
free(temp->item->key);
free(temp->item->value);
free(temp->item);
free(temp);
return it;
}
void free_linkedlist(LinkedList* list) {
LinkedList* temp = list;
while (list) {
temp = list;
list = list->next;
free(temp->item->key);
free(temp->item->value);
free(temp->item);
free(temp);
}
}
Теперь нужно добавить эти списки переполненных бакетов в хеш-таблицу. У каждого элемента должна быть одна такая цепочка, поэтому для всей таблицы мы добавим массив указателей LinkedList.
typedef struct HashTable HashTable;
// Define the Hash Table here
struct HashTable {
// Contains an array of pointers
// to items
Ht_item** items;
LinkedList** overflow_buckets;
int size;
int count;
};
Теперь, когда мы определили overflow_buckets, давайте добавим функции для их создания и удаления. Их также необходимо учитывать в старых функциях create_table() и free_table().
LinkedList** create_overflow_buckets(HashTable* table) {
// Create the overflow buckets; an array of linkedlists
LinkedList** buckets = (LinkedList**) calloc (table->size, sizeof(LinkedList*));
for (int i=0; i<table->size; i++)
buckets[i] = NULL;
return buckets;
}
void free_overflow_buckets(HashTable* table) {
// Free all the overflow bucket lists
LinkedList** buckets = table->overflow_buckets;
for (int i=0; i<table->size; i++)
free_linkedlist(buckets[i]);
free(buckets);
}
HashTable* create_table(int size) {
// Creates a new HashTable
HashTable* table = (HashTable*) malloc (sizeof(HashTable));
table->size = size;
table->count = 0;
table->items = (Ht_item**) calloc (table->size, sizeof(Ht_item*));
for (int i=0; i<table->size; i++)
table->items[i] = NULL;
table->overflow_buckets = create_overflow_buckets(table);
return table;
}
void free_table(HashTable* table) {
// Frees the table
for (int i=0; i<table->size; i++) {
Ht_item* item = table->items[i];
if (item != NULL)
free_item(item);
}
// Free the overflow bucket linked linkedlist and it's items
free_overflow_buckets(table);
free(table->items);
free(table);
}
Теперь перейдем к функции handle_collision().
Здесь есть два сценария. Если список элемента не существует, нам нужно создать такой список и добавить в него элемент.
В противном случае мы можем просто вставить элемент в список.
void handle_collision(HashTable* table, unsigned long index, Ht_item* item) {
LinkedList* head = table->overflow_buckets[index];
if (head == NULL) {
// We need to create the list
head = allocate_list();
head->item = item;
table->overflow_buckets[index] = head;
return;
}
else {
// Insert to the list
table->overflow_buckets[index] = linkedlist_insert(head, item);
return;
}
}
Итак, мы закончили со вставкой, и теперь нам также нужно обновить функцию поиска, так как нам, возможно, потребуется также просмотреть переполненные бакеты.
char* ht_search(HashTable* table, char* key) {
// Searches the key in the hashtable
// and returns NULL if it doesn't exist
int index = hash_function(key);
Ht_item* item = table->items[index];
LinkedList* head = table->overflow_buckets[index];
// Ensure that we move to items which are not NULL
while (item != NULL) {
if (strcmp(item->key, key) == 0)
return item->value;
if (head == NULL)
return NULL;
item = head->item;
head = head->next;
}
return NULL;
Итак, мы учли коллизии в функциях insert() и search(). На данный момент наш код выглядит так:
#include
#include
#include
#define CAPACITY 50000 // Size of the Hash Table
unsigned long hash_function(char* str) {
unsigned long i = 0;
for (int j=0; str[j]; j++)
i += str[j];
return i % CAPACITY;
}
typedef struct Ht_item Ht_item;
// Define the Hash Table Item here
struct Ht_item {
char* key;
char* value;
};
typedef struct LinkedList LinkedList;
// Define the Linkedlist here
struct LinkedList {
Ht_item* item;
LinkedList* next;
};
typedef struct HashTable HashTable;
// Define the Hash Table here
struct HashTable {
// Contains an array of pointers
// to items
Ht_item** items;
LinkedList** overflow_buckets;
int size;
int count;
};
static LinkedList* allocate_list () {
// Allocates memory for a Linkedlist pointer
LinkedList* list = (LinkedList*) malloc (sizeof(LinkedList));
return list;
}
static LinkedList* linkedlist_insert(LinkedList* list, Ht_item* item) {
// Inserts the item onto the Linked List
if (!list) {
LinkedList* head = allocate_list();
head->item = item;
head->next = NULL;
list = head;
return list;
}
else if (list->next == NULL) {
LinkedList* node = allocate_list();
node->item = item;
node->next = NULL;
list->next = node;
return list;
}
LinkedList* temp = list;
while (temp->next->next) {
temp = temp->next;
}
LinkedList* node = allocate_list();
node->item = item;
node->next = NULL;
temp->next = node;
return list;
}
static Ht_item* linkedlist_remove(LinkedList* list) {
// Removes the head from the linked list
// and returns the item of the popped element
if (!list)
return NULL;
if (!list->next)
return NULL;
LinkedList* node = list->next;
LinkedList* temp = list;
temp->next = NULL;
list = node;
Ht_item* it = NULL;
memcpy(temp->item, it, sizeof(Ht_item));
free(temp->item->key);
free(temp->item->value);
free(temp->item);
free(temp);
return it;
}
static void free_linkedlist(LinkedList* list) {
LinkedList* temp = list;
while (list) {
temp = list;
list = list->next;
free(temp->item->key);
free(temp->item->value);
free(temp->item);
free(temp);
}
}
static LinkedList** create_overflow_buckets(HashTable* table) {
// Create the overflow buckets; an array of linkedlists
LinkedList** buckets = (LinkedList**) calloc (table->size, sizeof(LinkedList*));
for (int i=0; isize; i++)
buckets[i] = NULL;
return buckets;
}
static void free_overflow_buckets(HashTable* table) {
// Free all the overflow bucket lists
LinkedList** buckets = table->overflow_buckets;
for (int i=0; isize; i++)
free_linkedlist(buckets[i]);
free(buckets);
}
Ht_item* create_item(char* key, char* value) {
// Creates a pointer to a new hash table item
Ht_item* item = (Ht_item*) malloc (sizeof(Ht_item));
item->key = (char*) malloc (strlen(key) + 1);
item->value = (char*) malloc (strlen(value) + 1);
strcpy(item->key, key);
strcpy(item->value, value);
return item;
}
HashTable* create_table(int size) {
// Creates a new HashTable
HashTable* table = (HashTable*) malloc (sizeof(HashTable));
table->size = size;
table->count = 0;
table->items = (Ht_item**) calloc (table->size, sizeof(Ht_item*));
for (int i=0; isize; i++)
table->items[i] = NULL;
table->overflow_buckets = create_overflow_buckets(table);
return table;
}
void free_item(Ht_item* item) {
// Frees an item
free(item->key);
free(item->value);
free(item);
}
void free_table(HashTable* table) {
// Frees the table
for (int i=0; isize; i++) {
Ht_item* item = table->items[i];
if (item != NULL)
free_item(item);
}
free_overflow_buckets(table);
free(table->items);
free(table);
}
void handle_collision(HashTable* table, unsigned long index, Ht_item* item) {
LinkedList* head = table->overflow_buckets[index];
if (head == NULL) {
// We need to create the list
head = allocate_list();
head->item = item;
table->overflow_buckets[index] = head;
return;
}
else {
// Insert to the list
table->overflow_buckets[index] = linkedlist_insert(head, item);
return;
}
}
void ht_insert(HashTable* table, char* key, char* value) {
// Create the item
Ht_item* item = create_item(key, value);
// Compute the index
unsigned long index = hash_function(key);
Ht_item* current_item = table->items[index];
if (current_item == NULL) {
// Key does not exist.
if (table->count == table->size) {
// Hash Table Full
printf("Insert Error: Hash Table is full\n");
// Remove the create item
free_item(item);
return;
}
// Insert directly
table->items[index] = item;
table->count++;
}
else {
// Scenario 1: We only need to update value
if (strcmp(current_item->key, key) == 0) {
strcpy(table->items[index]->value, value);
return;
}
else {
// Scenario 2: Collision
handle_collision(table, index, item);
return;
}
}
}
char* ht_search(HashTable* table, char* key) {
// Searches the key in the hashtable
// and returns NULL if it doesn't exist
int index = hash_function(key);
Ht_item* item = table->items[index];
LinkedList* head = table->overflow_buckets[index];
// Ensure that we move to items which are not NULL
while (item != NULL) {
if (strcmp(item->key, key) == 0)
return item->value;
if (head == NULL)
return NULL;
item = head->item;
head = head->next;
}
return NULL;
}
void print_search(HashTable* table, char* key) {
char* val;
if ((val = ht_search(table, key)) == NULL) {
printf("%s does not exist\n", key);
return;
}
else {
printf("Key:%s, Value:%s\n", key, val);
}
}
void print_table(HashTable* table) {
printf("\n-------------------\n");
for (int i=0; isize; i++) {
if (table->items[i]) {
printf("Index:%d, Key:%s, Value:%s", i, table->items[i]->key, table->items[i]->value);
if (table->overflow_buckets[i]) {
printf(" => Overflow Bucket => ");
LinkedList* head = table->overflow_buckets[i];
while (head) {
printf("Key:%s, Value:%s ", head->item->key, head->item->value);
head = head->next;
}
}
printf("\n");
}
}
printf("-------------------\n");
}
int main() {
HashTable* ht = create_table(CAPACITY);
ht_insert(ht, "1", "First address");
ht_insert(ht, "2", "Second address");
ht_insert(ht, "Hel", "Third address");
ht_insert(ht, "Cau", "Fourth address");
print_search(ht, "1");
print_search(ht, "2");
print_search(ht, "3");
print_search(ht, "Hel");
print_search(ht, "Cau");
print_table(ht);
free_table(ht);
return 0;
}
Удаление из хеш-таблицы
Давайте взглянем на функцию удаления данных из таблицы:
void ht_delete(HashTable* table, char* key);
Эта функция работает аналогично вставке. Нам нужно:
- Вычислить хеш-индекс и получить элемент.
- Если это NULL, нам ничего не нужно делать
- В противном случае, если для этого индекса нет цепочки коллизий, после сравнения ключей нужно просто удалить элемент из таблицы.
- Если цепочка коллизий существует, мы должны удалить этот элемент и соответствующим образом сдвинуть данные.
Мы не будем перечислять здесь слишком много подробностей, так как эта процедура включает только обновление элементов заголовка и освобождение памяти. Предлагаем вам попытаться реализовать это самостоятельно.
Предоставляем вам рабочую версию для сравнения.
void ht_delete(HashTable* table, char* key) {
// Deletes an item from the table
int index = hash_function(key);
Ht_item* item = table->items[index];
LinkedList* head = table->overflow_buckets[index];
if (item == NULL) {
// Does not exist. Return
return;
}
else {
if (head == NULL && strcmp(item->key, key) == 0) {
// No collision chain. Remove the item
// and set table index to NULL
table->items[index] = NULL;
free_item(item);
table->count--;
return;
}
else if (head != NULL) {
// Collision Chain exists
if (strcmp(item->key, key) == 0) {
// Remove this item and set the head of the list
// as the new item
free_item(item);
LinkedList* node = head;
head = head->next;
node->next = NULL;
table->items[index] = create_item(node->item->key, node->item->value);
free_linkedlist(node);
table->overflow_buckets[index] = head;
return;
}
LinkedList* curr = head;
LinkedList* prev = NULL;
while (curr) {
if (strcmp(curr->item->key, key) == 0) {
if (prev == NULL) {
// First element of the chain. Remove the chain
free_linkedlist(head);
table->overflow_buckets[index] = NULL;
return;
}
else {
// This is somewhere in the chain
prev->next = curr->next;
curr->next = NULL;
free_linkedlist(curr);
table->overflow_buckets[index] = head;
return;
}
}
curr = curr->next;
prev = curr;
}
}
}
}
Полный код
Наконец, мы можем посмотреть на полный код программы хеш-таблицы.
#include
#include
#include
#define CAPACITY 50000 // Size of the Hash Table
unsigned long hash_function(char* str) {
unsigned long i = 0;
for (int j=0; str[j]; j++)
i += str[j];
return i % CAPACITY;
}
typedef struct Ht_item Ht_item;
// Define the Hash Table Item here
struct Ht_item {
char* key;
char* value;
};
typedef struct LinkedList LinkedList;
// Define the Linkedlist here
struct LinkedList {
Ht_item* item;
LinkedList* next;
};
typedef struct HashTable HashTable;
// Define the Hash Table here
struct HashTable {
// Contains an array of pointers
// to items
Ht_item** items;
LinkedList** overflow_buckets;
int size;
int count;
};
static LinkedList* allocate_list () {
// Allocates memory for a Linkedlist pointer
LinkedList* list = (LinkedList*) malloc (sizeof(LinkedList));
return list;
}
static LinkedList* linkedlist_insert(LinkedList* list, Ht_item* item) {
// Inserts the item onto the Linked List
if (!list) {
LinkedList* head = allocate_list();
head->item = item;
head->next = NULL;
list = head;
return list;
}
else if (list->next == NULL) {
LinkedList* node = allocate_list();
node->item = item;
node->next = NULL;
list->next = node;
return list;
}
LinkedList* temp = list;
while (temp->next->next) {
temp = temp->next;
}
LinkedList* node = allocate_list();
node->item = item;
node->next = NULL;
temp->next = node;
return list;
}
static Ht_item* linkedlist_remove(LinkedList* list) {
// Removes the head from the linked list
// and returns the item of the popped element
if (!list)
return NULL;
if (!list->next)
return NULL;
LinkedList* node = list->next;
LinkedList* temp = list;
temp->next = NULL;
list = node;
Ht_item* it = NULL;
memcpy(temp->item, it, sizeof(Ht_item));
free(temp->item->key);
free(temp->item->value);
free(temp->item);
free(temp);
return it;
}
static void free_linkedlist(LinkedList* list) {
LinkedList* temp = list;
while (list) {
temp = list;
list = list->next;
free(temp->item->key);
free(temp->item->value);
free(temp->item);
free(temp);
}
}
static LinkedList** create_overflow_buckets(HashTable* table) {
// Create the overflow buckets; an array of linkedlists
LinkedList** buckets = (LinkedList**) calloc (table->size, sizeof(LinkedList*));
for (int i=0; isize; i++)
buckets[i] = NULL;
return buckets;
}
static void free_overflow_buckets(HashTable* table) {
// Free all the overflow bucket lists
LinkedList** buckets = table->overflow_buckets;
for (int i=0; isize; i++)
free_linkedlist(buckets[i]);
free(buckets);
}
Ht_item* create_item(char* key, char* value) {
// Creates a pointer to a new hash table item
Ht_item* item = (Ht_item*) malloc (sizeof(Ht_item));
item->key = (char*) malloc (strlen(key) + 1);
item->value = (char*) malloc (strlen(value) + 1);
strcpy(item->key, key);
strcpy(item->value, value);
return item;
}
HashTable* create_table(int size) {
// Creates a new HashTable
HashTable* table = (HashTable*) malloc (sizeof(HashTable));
table->size = size;
table->count = 0;
table->items = (Ht_item**) calloc (table->size, sizeof(Ht_item*));
for (int i=0; isize; i++)
table->items[i] = NULL;
table->overflow_buckets = create_overflow_buckets(table);
return table;
}
void free_item(Ht_item* item) {
// Frees an item
free(item->key);
free(item->value);
free(item);
}
void free_table(HashTable* table) {
// Frees the table
for (int i=0; isize; i++) {
Ht_item* item = table->items[i];
if (item != NULL)
free_item(item);
}
free_overflow_buckets(table);
free(table->items);
free(table);
}
void handle_collision(HashTable* table, unsigned long index, Ht_item* item) {
LinkedList* head = table->overflow_buckets[index];
if (head == NULL) {
// We need to create the list
head = allocate_list();
head->item = item;
table->overflow_buckets[index] = head;
return;
}
else {
// Insert to the list
table->overflow_buckets[index] = linkedlist_insert(head, item);
return;
}
}
void ht_insert(HashTable* table, char* key, char* value) {
// Create the item
Ht_item* item = create_item(key, value);
// Compute the index
unsigned long index = hash_function(key);
Ht_item* current_item = table->items[index];
if (current_item == NULL) {
// Key does not exist.
if (table->count == table->size) {
// Hash Table Full
printf("Insert Error: Hash Table is full\n");
// Remove the create item
free_item(item);
return;
}
// Insert directly
table->items[index] = item;
table->count++;
}
else {
// Scenario 1: We only need to update value
if (strcmp(current_item->key, key) == 0) {
strcpy(table->items[index]->value, value);
return;
}
else {
// Scenario 2: Collision
handle_collision(table, index, item);
return;
}
}
}
char* ht_search(HashTable* table, char* key) {
// Searches the key in the hashtable
// and returns NULL if it doesn't exist
int index = hash_function(key);
Ht_item* item = table->items[index];
LinkedList* head = table->overflow_buckets[index];
// Ensure that we move to items which are not NULL
while (item != NULL) {
if (strcmp(item->key, key) == 0)
return item->value;
if (head == NULL)
return NULL;
item = head->item;
head = head->next;
}
return NULL;
}
void ht_delete(HashTable* table, char* key) {
// Deletes an item from the table
int index = hash_function(key);
Ht_item* item = table->items[index];
LinkedList* head = table->overflow_buckets[index];
if (item == NULL) {
// Does not exist. Return
return;
}
else {
if (head == NULL && strcmp(item->key, key) == 0) {
// No collision chain. Remove the item
// and set table index to NULL
table->items[index] = NULL;
free_item(item);
table->count--;
return;
}
else if (head != NULL) {
// Collision Chain exists
if (strcmp(item->key, key) == 0) {
// Remove this item and set the head of the list
// as the new item
free_item(item);
LinkedList* node = head;
head = head->next;
node->next = NULL;
table->items[index] = create_item(node->item->key, node->item->value);
free_linkedlist(node);
table->overflow_buckets[index] = head;
return;
}
LinkedList* curr = head;
LinkedList* prev = NULL;
while (curr) {
if (strcmp(curr->item->key, key) == 0) {
if (prev == NULL) {
// First element of the chain. Remove the chain
free_linkedlist(head);
table->overflow_buckets[index] = NULL;
return;
}
else {
// This is somewhere in the chain
prev->next = curr->next;
curr->next = NULL;
free_linkedlist(curr);
table->overflow_buckets[index] = head;
return;
}
}
curr = curr->next;
prev = curr;
}
}
}
}
void print_search(HashTable* table, char* key) {
char* val;
if ((val = ht_search(table, key)) == NULL) {
printf("%s does not exist\n", key);
return;
}
else {
printf("Key:%s, Value:%s\n", key, val);
}
}
void print_table(HashTable* table) {
printf("\n-------------------\n");
for (int i=0; isize; i++) {
if (table->items[i]) {
printf("Index:%d, Key:%s, Value:%s", i, table->items[i]->key, table->items[i]->value);
if (table->overflow_buckets[i]) {
printf(" => Overflow Bucket => ");
LinkedList* head = table->overflow_buckets[i];
while (head) {
printf("Key:%s, Value:%s ", head->item->key, head->item->value);
head = head->next;
}
}
printf("\n");
}
}
printf("-------------------\n");
}
int main() {
HashTable* ht = create_table(CAPACITY);
ht_insert(ht, "1", "First address");
ht_insert(ht, "2", "Second address");
ht_insert(ht, "Hel", "Third address");
ht_insert(ht, "Cau", "Fourth address");
print_search(ht, "1");
print_search(ht, "2");
print_search(ht, "3");
print_search(ht, "Hel");
print_search(ht, "Cau"); // Collision!
print_table(ht);
ht_delete(ht, "1");
ht_delete(ht, "Cau");
print_table(ht);
free_table(ht);
return 0;
}
Результат выглядит так:
Key:1, Value:First address
Key:2, Value:Second address
3 does not exist
Key:Hel, Value:Third address
Key:Cau, Value:Fourth address
-------------------
Index:49, Key:1, Value:First address
Index:50, Key:2, Value:Second address
Index:281, Key:Hel, Value:Third address => Overflow Bucket => Key:Cau, Value:Fourth address
-------------------
-------------------
Index:50, Key:2, Value:Second address
Index:281, Key:Hel, Value:Third address
-------------------
Заключение
Надеемся, вы поняли, как можно реализовать хеш-таблицу с нуля на C/C++. Возможно, у вас получилось реализовать ее самостоятельно.
Советуем вам также попробовать на примере полученной таблицы использовать другие алгоритмы обработки коллизий и другие хеш-функции и проверить их производительность.
Скачать код, который мы рассмотрели в этом руководстве, можно на Github Gist.
Читайте также: Сравнение строк в C++: три основных метода
Tags: C++
